3.5 Scrum Principles
Scrum principles are the core guidelines for applying the scrum framework and should be used for maximum effect. The six scrum principles are:
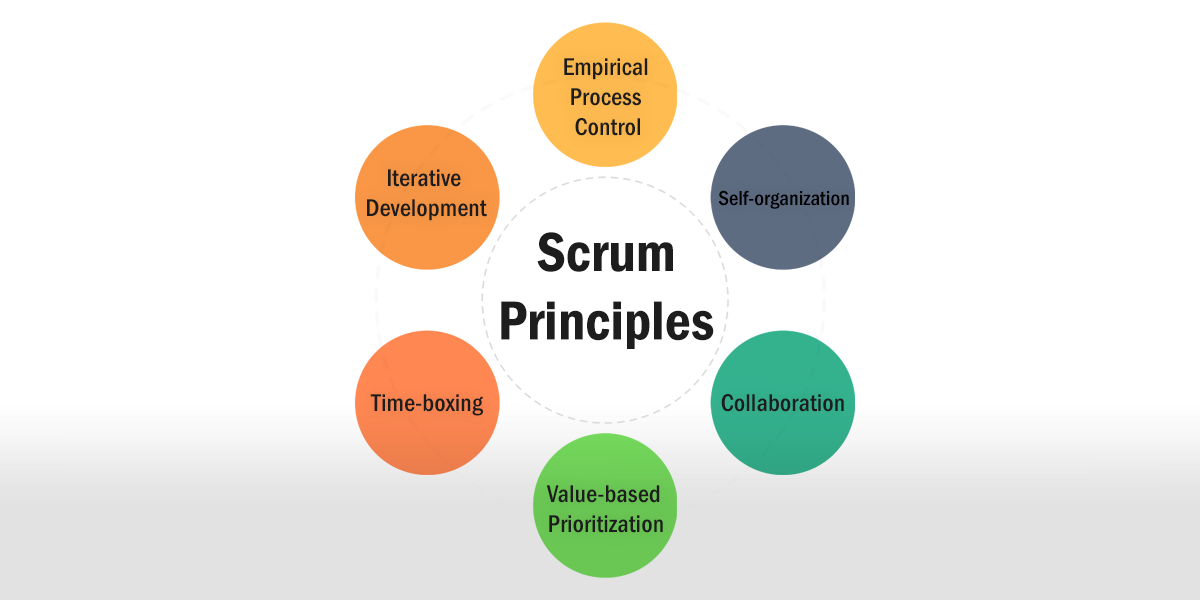
- Empirical Process Control emphasizes the core philosophy of scrum based on the three main ideas of transparency, inspection, and adaptation.
- Self-organization focuses on today’s workers, who deliver significantly greater value when self-organized. This results in better team buy-in and shared ownership; and an innovative and creative environment, which is more conducive for growth.
- Collaboration focuses on the three core dimensions related to collaborative work: awareness, articulation, and appropriation. It also advocates project management as a shared value-creation process with teams working and interacting together to deliver the greatest value.
- Value-based Prioritization highlights the focus of scrum to deliver maximum business value, from early on in the project and continuing throughout.
- Time-boxing describes how time is considered a limiting constraint in scrum, and is used to help effectively manage project planning and execution. Time-boxed elements in scrum include sprints, daily scrum meetings, sprint planning meetings, and sprint review meetings.
- Iterative Development emphasizes how to better manage changes and build products that satisfy customer needs. It also delineates the product owner’s and organization’s responsibilities related to iterative development.
